-
Reflection on the Class
-
Class Syllabus
-
Activities
-
Textbook
<
>
Reflection on the Class:
When working in Higher Education, it is important to focus on the students that are being served. This class really opened my eyes to the different demographics that make up today’s students as well as the differences between generations, attitudes towards higher education and the student development theory that is necessary in predicting persistence and student success.
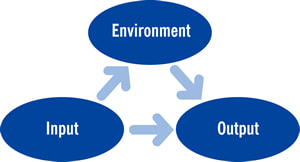
The entire class revolves around Alexander Astin’s theory on student involvement. The theory focus on three core concepts:
ASTIN'S I-E-O Model (1985)
When working in Higher Education, it is important to focus on the students that are being served. This class really opened my eyes to the different demographics that make up today’s students as well as the differences between generations, attitudes towards higher education and the student development theory that is necessary in predicting persistence and student success.
The entire class revolves around Alexander Astin’s theory on student involvement. The theory focus on three core concepts:
- Inputs – These are the inputs that students bring with them to college. Their demographics and experiences before college such as: race, gender, age, socioeconomic status, parental education, type of high school and high school preparedness, gpa, access to honors or AP classes, involvement in clubs and organizations, etcs.
- Environment – These are the interactions that students have in college. Relationship with faculty and staff, co-curricular involvement in clubs and organizations, the overall structure and governance of the institution, faculty/student ratio, student resources, etc.
- Outputs/Outcomes – These are the final results that a student gains from their experiences in college such as GPA, persistence, graduation rate, job acquisition after college, beliefs, values, attitudes and level of knowledge.
ASTIN'S I-E-O Model (1985)